What is a Network Switch ?
A network switch is a hardware that connects devices on a computer network by using packet switching to receive and forward data to the destination device. A network switch is a multiport network bridge that uses MAC addresses to forward data. It works at the data link layer of the OSI model. Unlike a router, a switch only sends data to the single device it is intended for which may be another devices. There are Layer 2 Network Switches , Layer 3 Network Switches and Layer 4 Network Switches also.
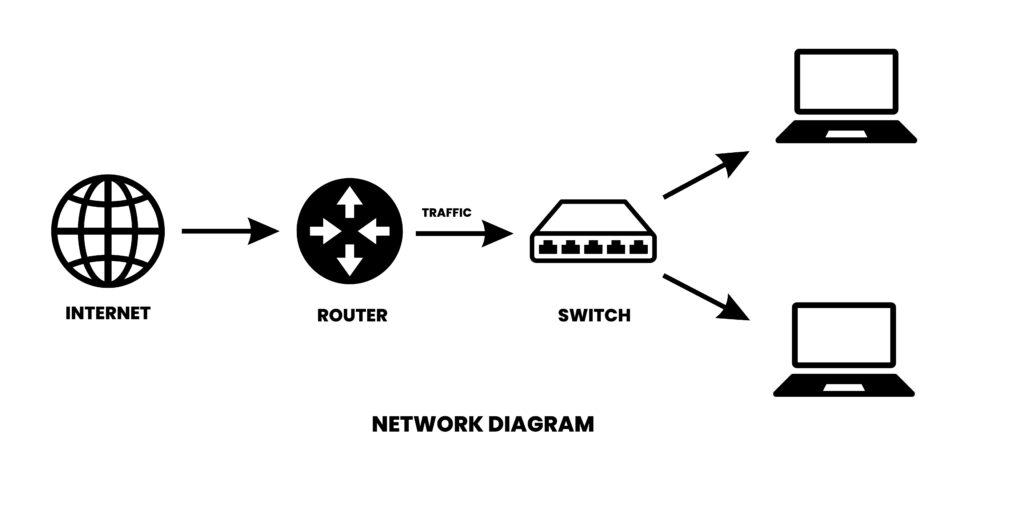


What is a Layer 2 Switch and Layer 3 Switch?
Network switch operates at layer 2 [ Data Link Layer ] or Layer 3 [ Network Layer ]. Layer 2 switches forward data based on the destination MAC address while layer 3 switches forward data based on the destination IP Address. We have few more switches that can work on both.
Layer 2 Switches and Layer 3 Switches both are in demand if we talk about Enterprise level. They connect to the devices in their networks using Ethernet cables. Ethernet cables are physical cables that plug into devices via Ethernet ports.
There are 8 Ports Switch, 24 Ports Switch and 48 Ports Switch also.
Difference Between Un-Managed Switch and Managed Switch
An unmanaged switch simply creates more Ethernet ports on a LAN, so that more local devices can access the Internet. Unmanaged switches pass data back and forth based on device MAC addresses.
A managed switch fulfills the same function for much larger networks, and offers network administrators much more control over how traffic is prioritized. They also enable administrators to set up Virtual LANs (VLANs) to further subdivide a local network into smaller chunks.
Type of Network Switches : PoE and Non PoE
Are you looking to upgrade your network infrastructure but unsure whether to opt for a PoE (Power over Ethernet) switch or a non-PoE switch? Understanding the differences between these two options can help you make an informed decision that aligns with your specific requirements. Let’s explore the key factors to consider :
Power Supply Efficiency:
PoE Switch: PoE switches deliver power and data over a single Ethernet cable, eliminating the need for separate power sources for connected devices like IP cameras, wireless access points, and VoIP phones. This streamlined setup reduces cable clutter and simplifies installation, making it ideal for environments where power outlets are limited.
Non-PoE Switch: Non-PoE switches require separate power sources for connected devices, which can lead to increased complexity in cable management and installation. While they offer flexibility in power supply options, they may not be as efficient in environments with numerous powered devices.
Cost Considerations:
PoE Switch: While PoE switches typically have a higher upfront cost compared to non-PoE switches, they can provide long-term cost savings by reducing the need for additional power infrastructure and simplifying maintenance. Additionally, the versatility of PoE switches makes them a cost-effective solution for scaling your network as your needs evolve.
Non-PoE Switch: Non-PoE switches generally have a lower initial investment cost, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious projects. However, it’s important to factor in the potential expenses associated with installing and maintaining separate power sources for connected devices over time.
Flexibility and Scalability:
PoE Switch: PoE switches offer greater flexibility and scalability by providing power and data transmission capabilities in a single device. This simplifies network management and allows for easier expansion of powered devices without the need for additional power infrastructure.
Non-PoE Switch: While non-PoE switches may offer flexibility in power supply options, they may not be as scalable or adaptable to changing network requirements. As the number of powered devices increases, the complexity of managing separate power sources can become a limiting factor.
In conclusion, the decision between a PoE switch and a non-PoE switch ultimately depends on your specific network needs, budget constraints, and future scalability requirements. By carefully evaluating factors such as power supply efficiency, cost considerations, and flexibility, you can choose the option that best suits your organization’s objectives. Whether you prioritize streamlined installation, cost-effectiveness, or scalability, Netonic Systems is here to help you navigate the complexities of network infrastructure and find the perfect solution for your business.